Elements and technical features » History » Version 15
« Previous -
Version 15/35
(diff) -
Next » -
Current version
HAENNIG, Gerald, 12/15/2015 07:40 AM
2.1 Elements¶
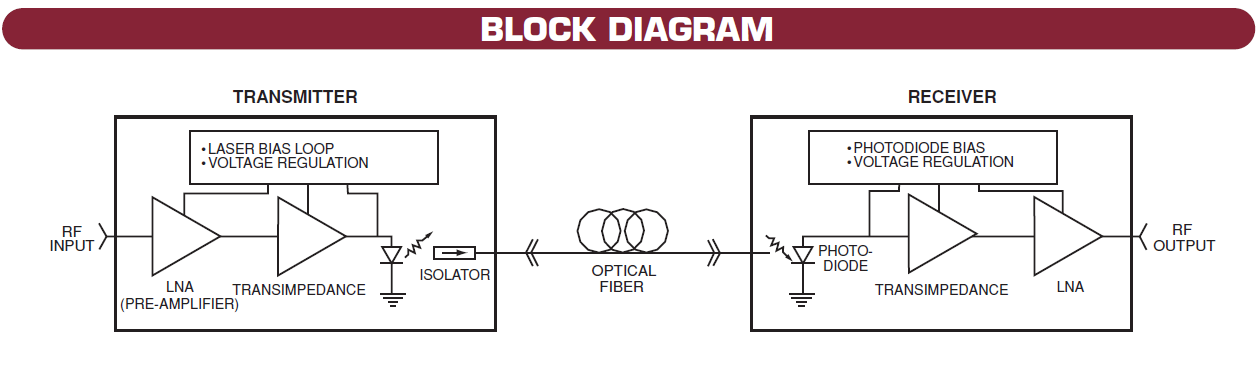
Figure 1. Optical Link (source Miteq).
- an optical transmitter ; it modulates input RF signal onto the optical wavelength intensity.
Optical intensity is varied either directly by varying Laser Diode current or indirectly through a Mach-Zehnder Modulator modulating a constant laser source. - fiber optic : in general, monomode fiber optic is used to avoid dispersion especially for long link. Morever, wavelengths around 1300 nm are used as dispersion is minimum in this region.
- an optical receiver : it is based on a photodectector. It detects RF modulation on the optical wavelength and outputs the RF signal.
Such an optical link is referred to as Radio Over Fiber (RoF), as well.
The main parameters for an optical link are gain, bandwidth, Noise Figure (NF) and Spurious Free Dynamic Range (SFDR).
MITEQ, Fiber optic products : https://www.miteq.com/docs/MITEQ_FiberOptic_c40.pdf
Main applications are- antenna remoting : for TV, signal is received on the antenna on the roof but actually demodulated in the tuner in the living room.
- signal distribution : for phased array radar application, it could be used to distribute the Local Oscillator to the different array elements.
Earth stations are based on an indoor/outdoor unit architecture. In our system we will count on:
- Outdoor: L-band reception antenna, the coaxial cable relying the antenna and the modulator transmitter (allows to convert from L-band to optic frequencies) and the 30m of Monomode FO.
- Indoor: consists of the receiver L-band/optic demodulator and the coaxial cable to rely the demodulator with the TV.

