FlexACM » History » Version 7
« Previous -
Version 7/10
(diff) -
Next » -
Current version
Cuadro, Juan Pablo, 12/15/2014 07:03 PM
FlexACM¶
As seen previously, the demodulator reports on the channel conditions (Es/N0 estimates) and the HUB subsequently selects the optimal MODCOD based on it. However, the choice of MODCOD is not only based upon comparison of the Es/N0 values with the thresholds for acceptable error rate performances,. It also takes in to account distortion that may be caused by non linearities from the channel or caused by a saturated transponder for example). Moreover, we add some margin in the link budget for safety.
Then, the MODCOD is chosen by comparing the estimated Es/N0 with the theoretical threshold of the MODCOD + distortion + margin, as shown in the figure below:
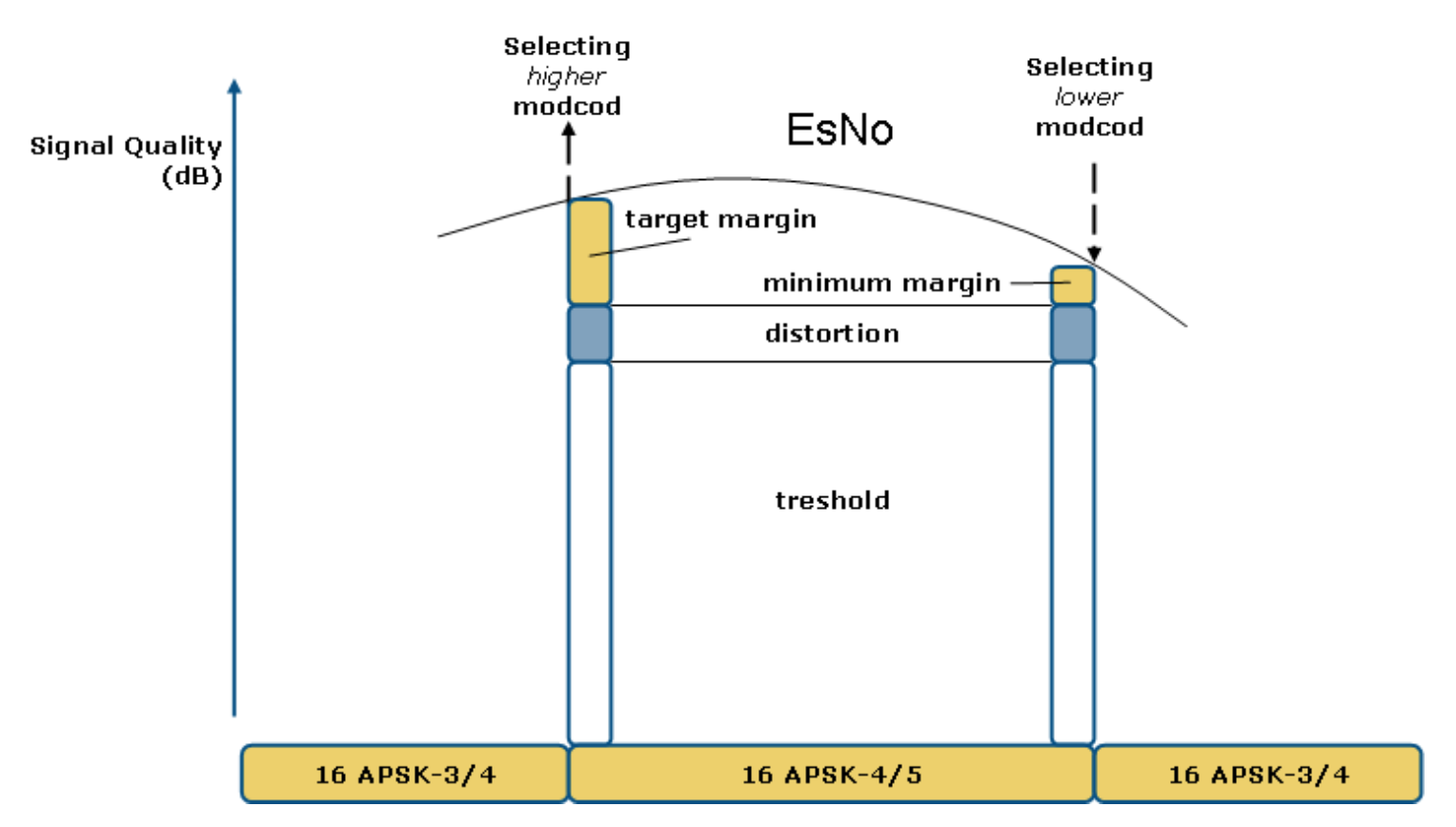
We can notice on this figure that the margin for selecting a higher MODCOD is higher than the one used to select a lower MODCOD. This is advised by the constructor to create hysteresis and avoid toggling of MODCODs for specific values of Es/N0.
Distortion is estimated thanks to the proprietary NoDE (Noise and Distorsion estimator) feature implemented in the modem, margins can be set up by the user and the table below shows the different thresholds for different MODCODs:
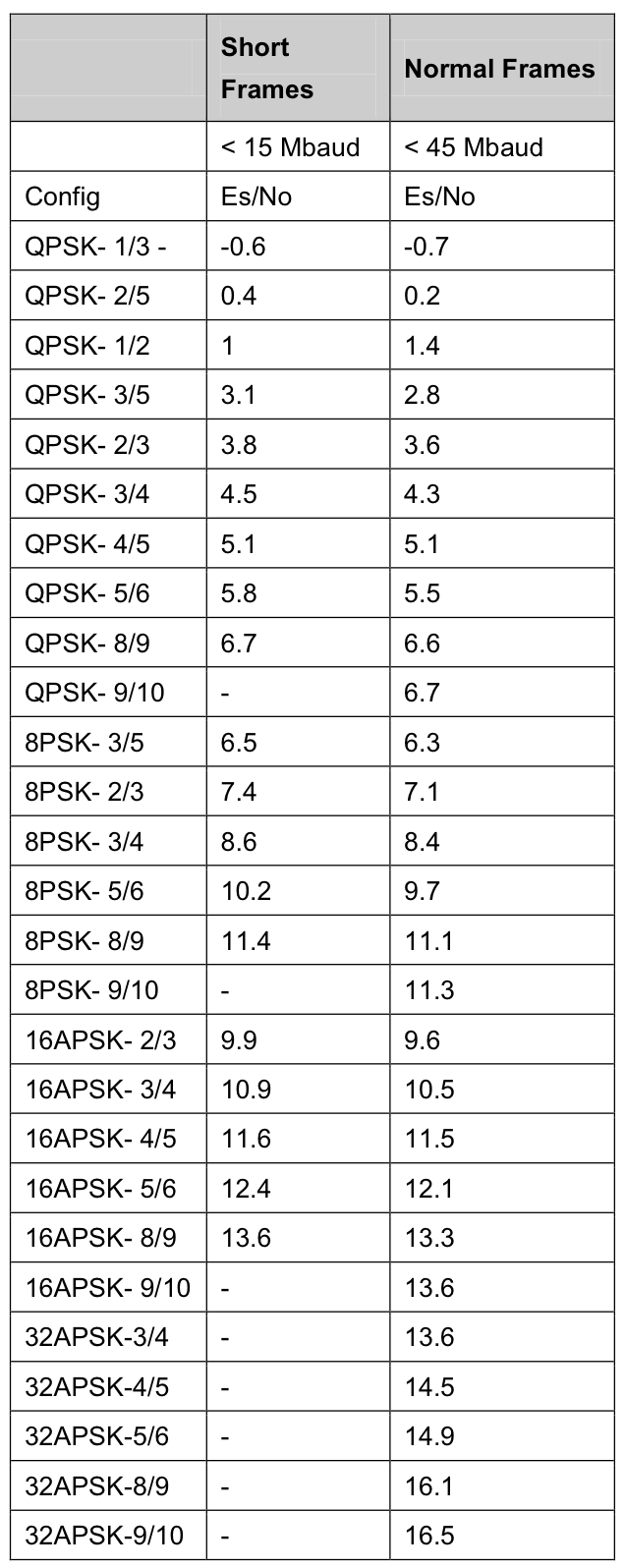
Note that these are the minimum Es/N0 values in order to have a quasi-error-free (QEF) transmission which ranslates into a packet error rate PER = 10 -5
Once the optimal MODCOD has been estimated at the demodulator, this information is sent back to the emitter side. Two options are possible: in-band or out-band signaling. This last one does not send the signaling messages back via the satellite but use another possible links (via a terrestrial network for example); it is not the one chosen for this project. We used in-band signaling, consisting in sending the MODCOD signaling messages directly via the return channel of the satellite link as non routable encapsulated IP packets.
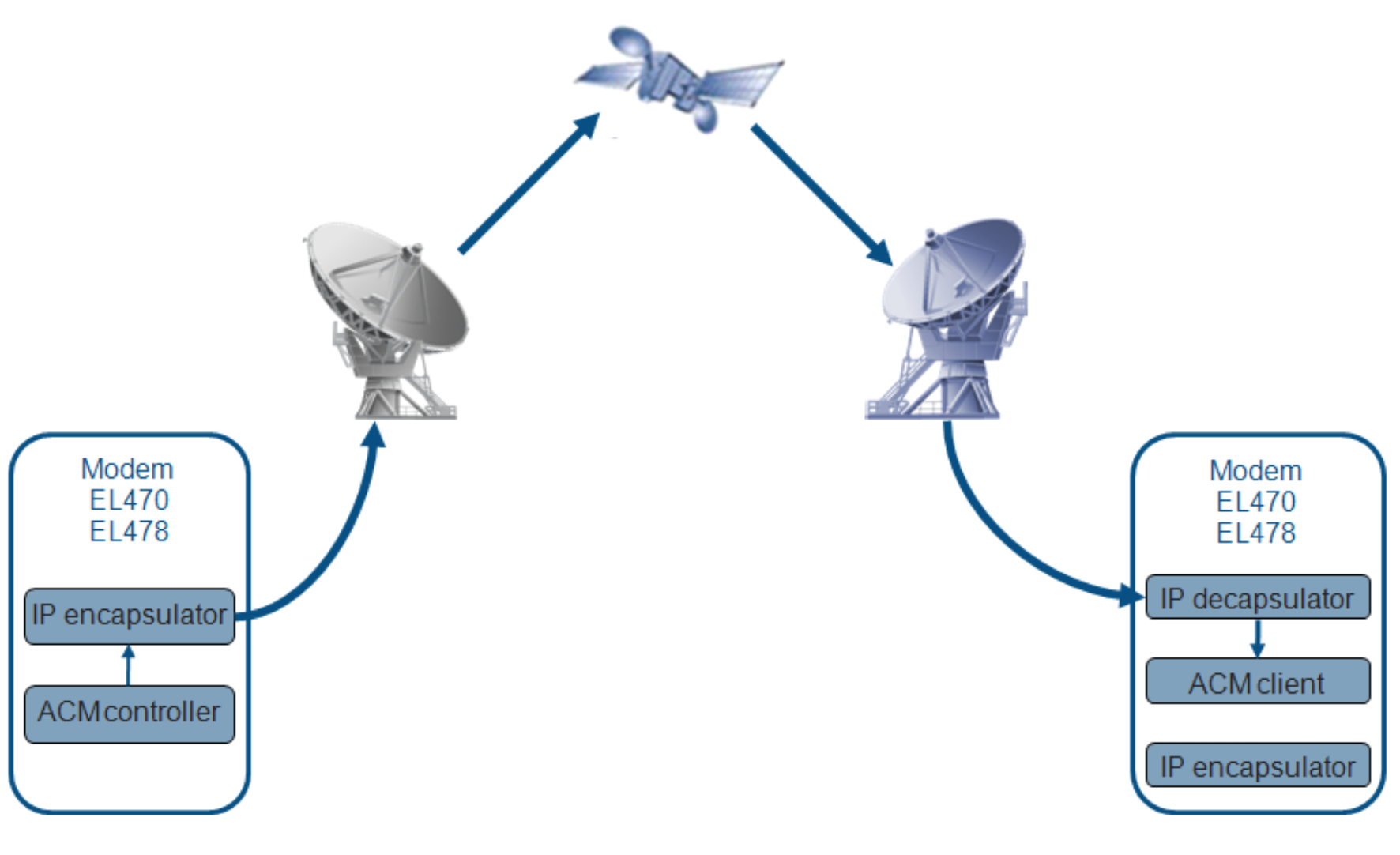
FlexACM In-band signalling on the forward link
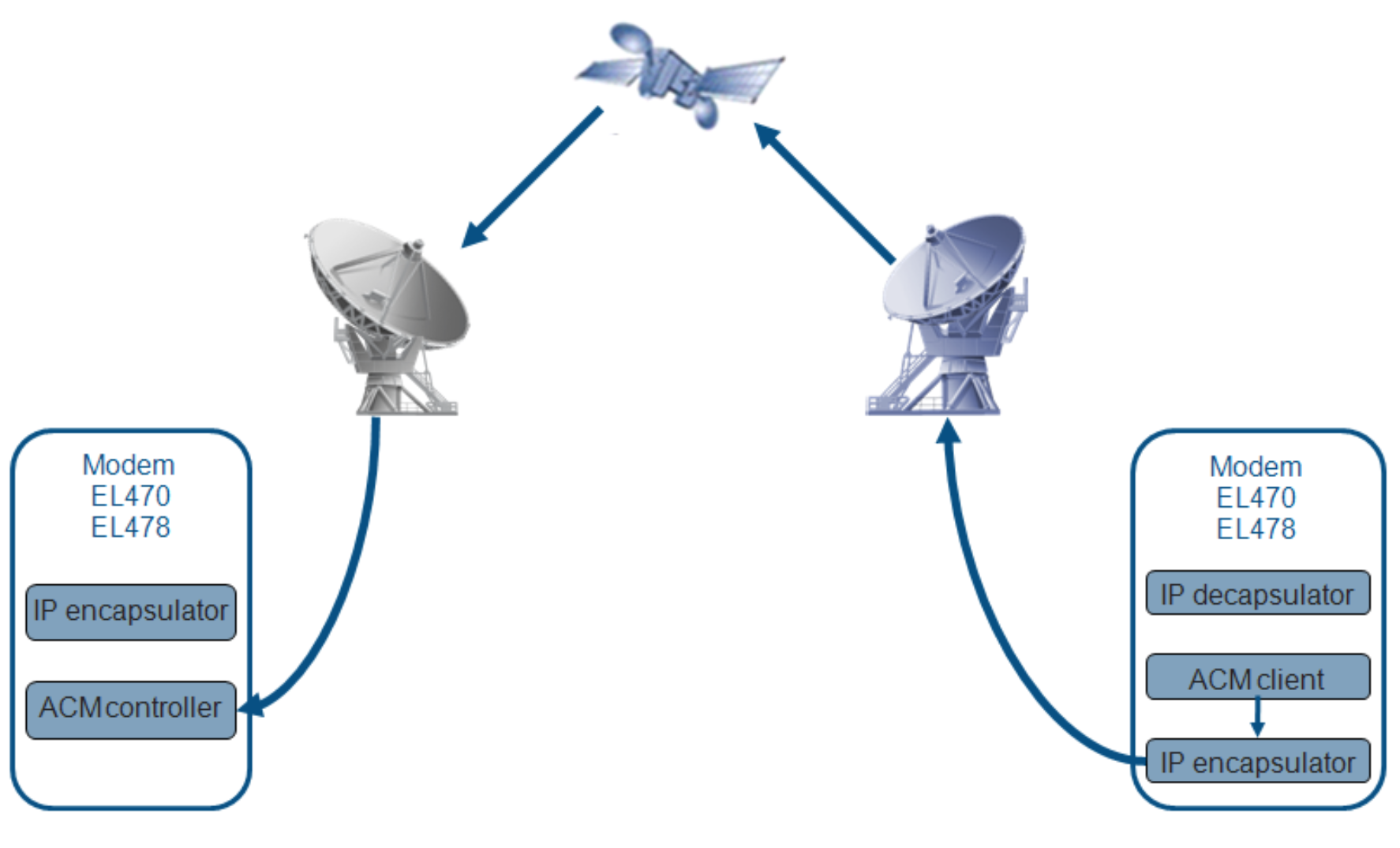
FlexACM In-band signalling on the return link
